At NVIDIA GTC 2023, HP and Vanderbilt University, who were provided with products by HP, had an enlightening conversation about data science and technology in the field of microscopy. While advancing computational technology has improved over the past decades, there is so much data being produced now that it is nigh-overwhelming for even the most updated solutions.
Now available on-demand, this NVIDIA GTC session focused on practical solutions for utilizing new data science technologies and featured Alex Duncan, Product Manager at HP and Bryan Millis Ph.D., Research Associate Professor & Associate Director of Science and Technology at Vanderbilt University.
Duncan kicked off the discussion by speaking about some of the challenges in data science. These include lack of available GPU instances, local systems that have underpowered compute, and bandwidth variability or constraints.
“At HP, we’re focused on enhancing model training with local computing power,” elucidated Duncan. HP has purpose-built data science workstations with software solutions like HP Anyware integrated into them. Duncan previewed the powerful HP Z8 Fury G5 workstation featuring up to 4 NVIDIA RTX™ A6000 GPUs, which can train more data iterations in less time, and computes larger batches of data within those iterations.
Bryan Millis was representing the Biophotonics Center of Vanderbilt University who “serve the biomedical research and clinical communities by trying to address pretty complex research and clinical problems with light-based solutions.” He spoke about how centralized solutions and high-performance graphics yield opportunities for biomedical researchers across the globe.
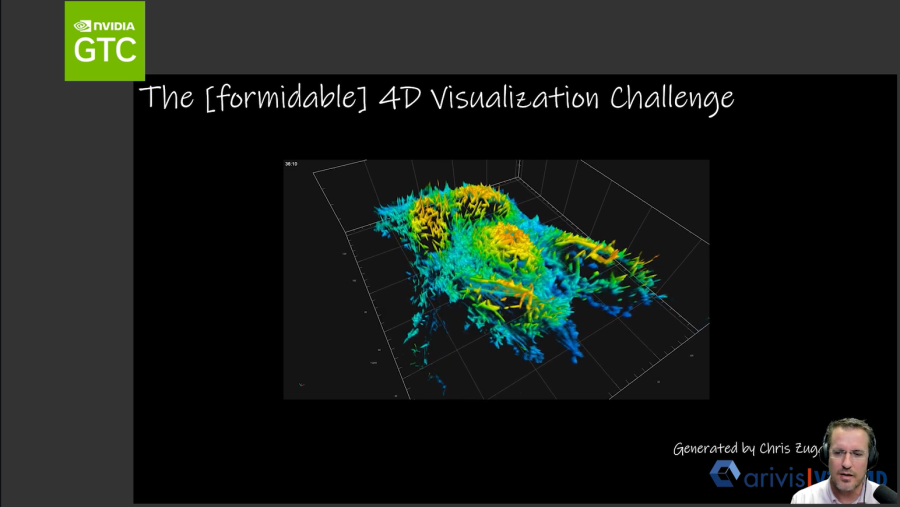
Millis outlined the technology needs of his team at Vanderbilt University. The team routinely uses CAD programs to design microscopes, but they also analyze and present findings from millions of points of data. This data often takes the form of real-time evolving diagrams.
Vanderbilt University built a rack of workstations that has CPU and GPU compute configurations so users can patch into the type of compute they require to do their work from wherever in the world they are. They use HP Anyware to access the compute resources from the university’s centralized data storage.
Some of the outcomes Vanderbilt University have experienced include time saved, more efficient workflows, being able to run more parallel models, the ability to train models for longer and for more precision and accuracy.
“In today’s remote world, there are experiences around remoting that enable more efficient workflows to be performed,” added Duncan as he introduced HP Anyware.
Based on PC-over-IP (PCoIP®) technology, HP Anyware is a digital workspaces software that works seamlessly with data science solutions on HP workstations to enhance workflows and address many of the remoting challenges data scientists face. Staff can work collaboratively from anywhere, knowing that sensitive information never leaves the data center and work can never be lost or stolen. Only encrypted pixels are transmitted from agent to client device, secured using AES 256 encryption.
Find out more about HP Anyware for digital workspaces here.
Learn more about how Z workstations empowers data scientists to compute larger data and how HP Anyware keeps data scientists productive and efficient wherever they work with Vanderbilt University’s case study. Watch the complete session at NVIDIA GTC session here.